In the ever-evolving world of software development, building scalable and resilient microservices has become essential. Java Spring Boot, Confluent Kafka, and Amazon Web Services (AWS) Elastic Container Service (ECS) are powerful technologies that, when combined, enable you to create a robust and flexible infrastructure for your microservices. In this blog article, we’ll explore how to set up a system that integrates Java Spring Boot with Confluent Kafka on AWS ECS using CloudFormation.
The technology stack
Before we dive into the details, let’s take a closer look at the technologies we’ll be using:
1. Java Spring Boot
Spring Boot is a popular framework for building microservices and creating stand-alone Spring applications. It simplifies the development process and provides a range of features to help you create robust and scalable applications.
2. Confluent Kafka
Kafka is a distributed streaming platform that allows you to build real-time data pipelines and streaming applications. Confluent Kafka is a popular distribution of Kafka that simplifies its deployment and management.
3. AWS ECS
Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) is a fully managed container orchestration service. It makes it easy to run, stop, and manage Docker containers on a cluster of Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances.
4. AWS CloudFormation
CloudFormation is an AWS service that helps you model and set up your AWS resources. It allows you to define your infrastructure as code, making it easy to provision and manage your resources.
Integration architecture
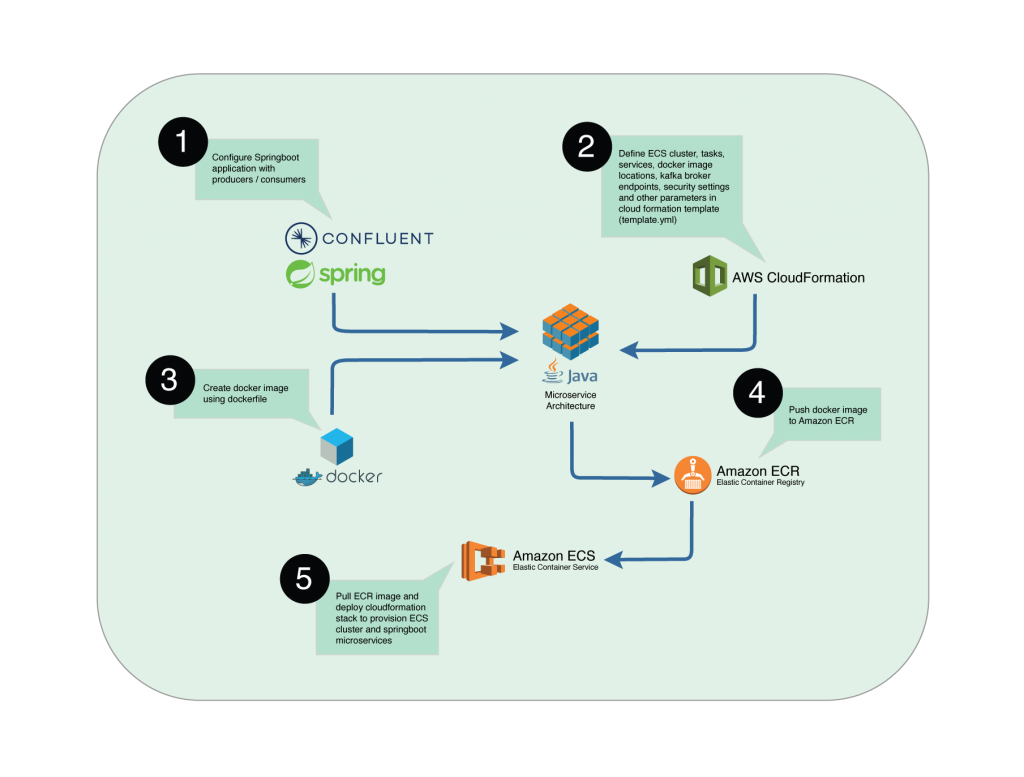
Setting up Java Spring Boot microservices
1. Developing a Spring Boot application
Begin by developing your Java Spring Boot microservices. This could be a simple RESTful service, or a more complex application, depending on your requirements. Ensure that your application is designed to be containerised using Docker, as you will be deploying it to ECS.
2. Containerizing the application
Create a Docker image for your Spring Boot application. You can use tools like Dockerfile to define the image and package your application along with its dependencies.
2.1 Below is a sample Dockerfile to package an application with dependencies
FROM public.ecr.aws/amazoncorretto/amazoncorretto:17.0.6
RUN mkdir -p /usr/app/$APPLICATION_NAME
WORKDIR /usr/app/$APPLICATION_NAME
USER root
COPY ./target/*.jar $APPLICATION_NAME
EXPOSE 8080
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-Djavax.net.debug=none", "-jar", $APPLICATION_NAME"] 3. Pushing the Docker Image to a Container Registry
Once your Docker image is ready, push it to a container registry like Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR). ECR provides a secure and scalable container image registry for your applications.
3.1 Build a docker image and push it to ECS
Check ECR account
ECR_REPO=$(aws sts get-caller-identity --query Account --output text).dkr.ecr.ap-southeast-2.amazonaws.com/REPO_NAMEDocker login
aws ecr get-login-password --region ap-southeast-2 | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin $ECR_REPOBuild Docker Image
docker buildx build --platform linux/amd64 -t ${IMAGE_NAME}
docker tag $IMAGE_NAME $ECR_REPO/${IMAGE_NAME}:$BUILD_VERSIONPush Docker Image
docker push $ECR_REPO/${IMAGE_NAME}:$BUILD_VERSION Setting up a Confluent Kafka cluster
Using Confluent Kafka, set up a Kafka cluster on AWS or another cloud provider of your choice [Eg: Confluent cloud]. Configure the necessary topics, partitions, and replication factors based on your application’s needs.
Note: As a Confluent Elite Partner, LimePoint excels in assisting clients to establish cloud-based solutions using Confluent Kafka. Reach out to us for specialised guidance.
Deploying on AWS ECS with CloudFormation
Now that you have your Spring Boot microservices and Confluent Kafka cluster set up, it’s time to deploy them on AWS ECS using CloudFormation.
1. Define your infrastructure as code
Create a CloudFormation template that defines your ECS cluster, tasks, services, and any other resources you need. Be sure to specify the necessary parameters, such as the Docker image locations, Kafka broker endpoints, and security settings.
Note: As a Confluent Premier Partner, LimePoint excels in assisting clients to establish cloud-based solutions using Confluent Kafka. Reach out to us for specialised guidance.
2. Deploy the stack
Use the AWS CloudFormation console or the AWS Command Line Interface (CLI) to deploy your CloudFormation stack. This will provision your ECS cluster and deploy your Spring Boot microservices.
Sample CloudFormation stack deployment via AWS CLI
Check the Docker image version on ECR
IMAGE_VERSION=$(aws ecr describe-images --repository-name $ECR-REPO/${STACK_NAME} --query 'sort_by(imageDetails,& imagePushedAt)[-1].imageTags[0]')Update CloudFormation stack
docker run --rm \
-v `pwd`:/cwd \
-e AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID -e AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY -e AWS_SESSION_TOKEN \ -e AWS_REGION \ realestate/stackup:1.4.6 $STACK_NAME up \ -t fargate.yml \ -o ImageVersion=$IMAGE_VERSION3. Monitor and scale
Once your services are up and running, use AWS services like Amazon CloudWatch and AWS Auto Scaling to monitor and scale your microservices based on metrics like CPU usage or message queue backlog.
Conclusion
Integrating Java Spring Boot with Confluent Kafka on AWS ECS using CloudFormation provides a scalable and reliable architecture for building microservices. It allows you to process real-time data efficiently, handle heavy workloads, and adapt to changing demands. By following the steps outlined in this blog, you can build a powerful infrastructure that’s capable of handling modern, data-driven applications.
Discover how we’ve aided our clients in seamlessly integrating AWS ECS, Confluent Kafka, and Java microservices. Connect with us for details


